Table Of Content

You can also use this type of research to map prevailing variables that exist at a particular given point—for example, cross-sectional data on past drinking habits and a current diagnosis of liver failure. The people in that extended family are used to determine what is happening in real-time at the moment. Groups can be affected by cohort differences that arise from the particular experiences of a group of people. For example, individuals born during the same period might witness the same important historical events, but their geographic regions, religious affiliations, political beliefs, and other factors might affect how they perceive such events. We encourage the readers to go through some of these studies to understand the design and analysis of cross-sectional studies.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF THIS STUDY
Conclusions MUH residents in urban Bangladesh highly demanded smoke-free housing. The data collected through the survey was anonymized with a unique identification code and deleted immediately after saving the research data. Stored research data was encrypted and would be permanently deleted three years after the completion of the study. Participants’ mobile phone numbers that were collected to provide rewards were permanently deleted immediately after the rewards were sent. Cross-sectional studies do not allow researchers to track changes over time, making them unsuitable for studying temporal relationships. The primary goal of a cross-sectional study is to describe the prevalence of a specific condition or characteristic within a defined population at a particular moment in time.
Cardiovascular disease behavioural risk factors in rural interventions: cross-sectional study Scientific Reports - Nature.com
Cardiovascular disease behavioural risk factors in rural interventions: cross-sectional study Scientific Reports.
Posted: Thu, 17 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
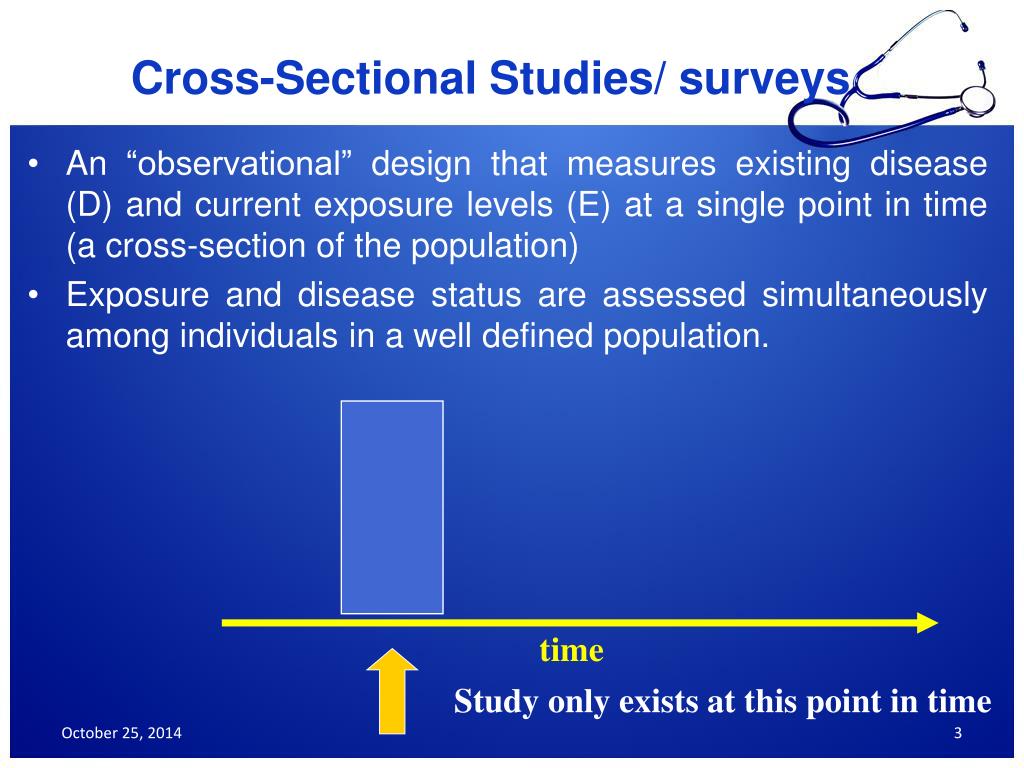
Strengths of a Cross-sectional Study
The increasing obesity rates may have modestly increased the prevalence of depressive symptoms in the general population [18]. However, there is currently no data to explore the association between BMI and mental health among nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic. To fill this gap, we conducted a large cross-sectional study to explore the association between BMI and mental health among nurses in China during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, simulation-based education does not only bring the aforementioned positive outcomes to participating students.
Table 1:
Second, the authors are thankful to the management committees of MUH complexes for their permission and cooperation in data collection. Finally, the authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Institute for Global Tobacco Control, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health (JHSPH), Baltimore, USA. Table 1 shows the distribution of the respondents by sociodemographic and smoking-related characteristics.
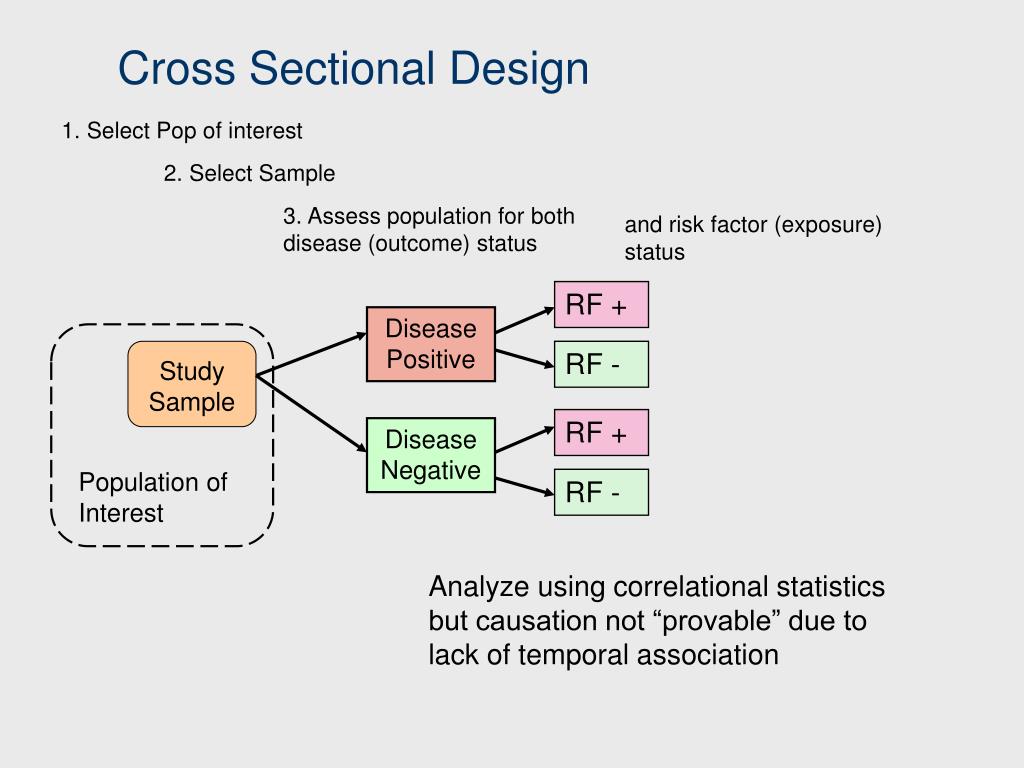
Poor mental health often affects regular activities and probably results in poor professional performance. Given the detrimental effects of depression and anxiety on physical and mental health, it is important to explore the relevant factors, and to thereby contribute toward preventing the development of mental health disorders [5]. 2) Differences in simulation educational satisfaction according to the general characteristics of the participants were analyzed by t-test and one-way ANOVA, and Sheffe’s test was used as the post hoc test. In an analytical cross-sectional study, the odds ratio can be used to assess the strength of an association between a risk factor and health outcome of interest, provided that the current exposure accurately reflects the past exposure. Another purpose of a cross-sectional study is to simultaneously describe multiple characteristics. For instance, it can be employed to explore whether factors like excessive screen time, social media use, and resulting social pressures are linked to specific outcomes such as anxiety.
Training and data collection
The study revealed that simulation design, flow, and simulation educational satisfaction are positively related and that flow has a partial mediating effect on the relationship between simulation design and simulation educational satisfaction. The results suggest that immersion in simulation situations plays a mediating role in the relationship between simulation instructional design and simulation training satisfaction. To increase the simulation educational satisfaction, the scale should be designed by considering the learning goals and contents, support methods during simulation, problem-solving methods, feedback, realism, and building an immersion strategy. First, further research should assess various variables suggested by the NLN/Jeffries simulation theory. Second, it is necessary to develop faculty development programs to improve the ability to apply simulation design and teaching strategies and to determine their effectiveness. In this study, nursing students were deeply engaged in the simulation and satisfied with their simulation-based education when the simulation design was adequate.
Data availability
The GAD07 questionnaire comprises 7 items, with each item being responded to on a 4-point Likert-type scale ranging from 0 (indicating never) to 3 (indicating always). A GAD07 standardized score of 10 or higher was used to characterize the presence of significant anxiety symptoms. The Cronbach's α coefficients for the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) were 0.951 and 0.928, respectively.
Researchers leverage different types of research studies to gather and analyze data. The characteristics you want to observe and your research goals dictate the best type of study to use. Cross-sectional studies, for instance, are vital when researching groups of people at a single point in time.
Measurement of depression and anxiety
Studies on nursing students in Korea have reported that nursing students who participated in simulation-based education felt nervous and anxious, overwhelmed and embarrassed, and guilty about making mistakes [5, 8, 9]. Stress and low self-confidence due to simulation-based education [10] and the idea that others are watching them lead to anxiety, resulting in passivity when participating in simulations with peers [11]. Additionally, high anxiety levels experienced during the simulation process can drive learners into a panic, which leads to negative learning effects and decreases simulation educational satisfaction [12, 13]. Cross-sectional studies are observational studies that analyze data from a population at a single point in time. They are often used to measure the prevalence of health outcomes, understand determinants of health, and describe features of a population. Unlike other types of observational studies, cross-sectional studies do not follow individuals up over time.
In contrast, longitudinal research takes considerable time because data is collected across numerous periods (potentially decades). Although longitudinal and cross-sectional studies are both observational, they are relatively different types of research design. This study type is commonly used in clinical research, business-related studies, and population studies. This may be a single snapshot for one point in time or may look at a situation at one point in time and then follow it up with another or multiple snapshots at later points; this is then termed a repeated cross-sectional data analysis.
MUH residents who stayed at home for more than 12 hours per day were 2.6 times more likely to prefer a smoke-free building policy than those who stayed at home for 12 hours or less per day (95% CI 1.035 to 6.493). Non-smokers were 3.2 times more likely to prefer a smoke-free building policy than smokers (95% CI 1.317 to 7.582). Residents whose family members smoked were 3.0 times more likely to favour a smoke-free building policy than those whose family members did not smoke (95% CI 1.058 to 8.422). Similarly, MUH residents with at least one child under 15 years of age in the household were 70.0% less likely to choose a common area policy than those with no child under 15 years of age in the household (95% CI 0.152 to 0.778). Females were 3.7 times more likely to prefer a smoke-free unit policy than their male counterparts (95% CI 1.024 to 13.188). Dhaka City has a significantly larger number of MUH complexes than any other divisional city in Bangladesh, although the correct proportion was unidentified due to data scarcity.
The standards explain that simulation design influences simulation experience within the overall context of simulation education [4], which supports the findings of this study. Several studies with domestic and international nursing students have demonstrated that the better the simulation design, the higher the flow and satisfaction [15, 17, 30], suggesting that simulation design is critical to achieving positive outcomes in simulation-based education. The average score of 4.17 ± 0.45 was greater than the results of several studies on Korean nursing students [12, 16, 20, 29]. Thus, it suggests that Korean nursing education is moving toward simulation-based instructional design. The simulation educational satisfaction score in this study was 62.90 ± 6.93, which was higher than the scores of 57.12 ± 8.21 [8] and 57.26 ± 6.53 [17] in previous studies using the same scale. The higher the satisfaction with the major, the higher the satisfaction with clinical practice [25], and the higher the satisfaction with university life, the higher the simulation educational satisfaction.
Physical activity and nutrition in relation to resilience: a cross-sectional study Scientific Reports - Nature.com
Physical activity and nutrition in relation to resilience: a cross-sectional study Scientific Reports.
Posted: Sat, 27 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
For example, respondents might not disclose certain behaviors or beliefs out of embarrassment, fear, or other limiting perception. A study by Sardana et al. evaluated the antibiotic resistance in isolates of Propionibacterium acnes in a tertiary care hospital in India. They recruited 80 patients of acne vulgaris, collected specimen for isolation from open or closed comedones. These specimens were then cultured, the growth identified, and antibiotic susceptibility and resistance were assessed.

No comments:
Post a Comment